| Enrollment extended: Enrollment is open until May 6, 2012 | |
 |
|
| FIELD GUIDES. | Knowledge Transfer, Community Based Adaptation, and Field Guides |
 |
Knowledge to be transferred in community-based adaptation needs to be a two-way transfer. Experts and remote, rural community members have different positions and expectations. Bridging these requires mutual understanding—understanding that can be complicated by culture, language and experience.
Developing a short, concise field guide helps in a number of ways. It allows you to compile how-to information from diverse sources into a guide that best fits your community’s context, and gives you the basis for a workshop plan.
|
| Field Guide 1. | Participatory Capacity and Vulnerability Assessments (PCVA) |
 |
CBA combines local climate knowledge and scientific climate knowledge in a way that will empower community members to take charge in an effective bottom-up campaign of adapting to climate change. Their project will be sustainable—as this bottom-up approach gives them project ownership. How do we learn about local climate knowledge?
The first step is to facilitate a PCVA workshop which will help in exchanging knowledge about the community’s vulnerabilities and capacities. What are the hazards and risks they face?
|
| Field Guide 2. | Participatory Mapping for Soil and Water Resources |
 |
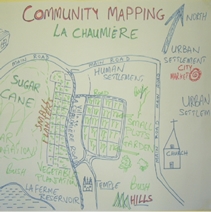
Participatory mapping is an excellent way of learning in greater detail about a community, their resources, the hazards they face, and how the village, farm fields, roads, forests, water sources, and climate challenges interrelate. It’s also an excellent way for community members to see their assets and vulnerabilities through a new lens.
Participatory mapping is an inclusive tool: all workshop participants can engage in the activity as it’s very visual—non-readers won’t be sidelined. |
| Field Guide 3. | Simple Techniques for Soil and Water Conservation |
 |
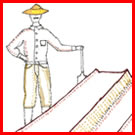
Subsistence farmers suffer not only from depleted soils but from challenges with water: too little water, too much water, and erosion from water. This field guide looks at different ways of managing water and conserving soil by developing barriers on farm fields for stopping the flow of water allowing it to percolate into the soil and build up soil moisture.
|
| Field Guide 4. | Developing a Community-Based Disaster Risk Reduction Plan |
 |
If a disaster forced an evacuation—people need to know when to evacuate, where to go where it’s safe, what to do with their valuable possessions and assets, what to take with them & what to do when they get to shelter.
It is estimated that over 50% of all disasters are now related to extreme weather events. Because of this, disaster risk reduction should be an integral part of adaptation projects.
|
| Field Guide 5. | Diversifying Livelihoods |
 |
Diversifying livelihoods is a good option for increasing resilience in the face of climate change challenges. For example, reduced agricultural production can be offset buy new climate-proof livelihoods.There are many micro-lending and micro-enterprise programs in the developing world able to assist.
However, not everyone is an entrepreneur. Another challenge is that frequently, people think of a product they would like to sell, begin making it, and then have trouble finding customers. There are several simple techniques for addressing these challenges—including climate-proofing current livelihoods.
|
| Routledge CBA Book: | A Field Guide to Community Based Adaptation by Tim Magee |
 |
This how-to field course in a book is arranged in a step-by-step progression that leads readers through problem assessment, project design, implementation, and community take over. Chapters have the tools needed by field staff and their community partners to complete sequential, concrete steps in developing a real project from the ground up. Routledge has announced a December 1 book launch.
|
In addition, the book includes a range of short field guides—like the five in this newsletter—containing activities complete with illustrations, how-to information, and workshop plans on universal climate challenges that communities face in the areas of water, food security, agriculture, disaster risk reduction, and livelihood diversification.
Learn more about design and implementing CBA projects.